spring源码解析(一)---占位符解析替换
一、结构类图
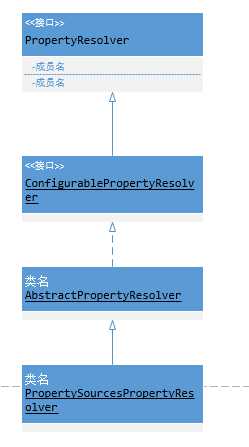
①、PropertyResolver : Environment的顶层接口,主要提供属性检索和解析带占位符的文本。bean.xml配置中的所有占位符例如${}都由它解析
②、ConfigurablePropertyResolver : 该接口定义了如何对组件本身进行配置。如:刚刚提到获取value时可以指定任意类型,这依赖于ConversionService进行类型转换,当前接口就提供了对ConversionService的设置和获取。另外,可以配置属性占位符的格式,包括:占位符前缀(默认为"${")、占位符后缀(默认为"}")、占位符值分隔符(默认为":",用于分隔propertyName和defaultValue)。组件还可以设置哪些属性是必须存在的,还可以校验必须存在的属性是否真的存在(不存在的话会抛出异常)
③、AbstractPropertyResolver : 实现了ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口的所有方法
④、PropertySourcesPropertyResolver : 以PropertySources属性源集合(内部持有属性源列表List<PropertySource>)为属性值的来源,按序遍历每个PropertySource,获取到一个非null的属性值则返回
二、demo示例
public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = System.getProperties(); properties.setProperty("prefixName", "read-code"); ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:${prefixName}-spring.xml"); ReadCodeService readCodeService = (ReadCodeService) ac.getBean("readCodeService"); readCodeService.say(); }
三、源码剖析
1、入口 :
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 构造函数setConfigLocations
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } }
2、AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
①、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数调用它的基类AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.setConfigLocations
/** * Set the config locations for this application context. * <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate. */ public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) { if (locations != null) { Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null"); this.configLocations = new String[locations.length]; for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) { this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim(); // 解析路劲 } } else { this.configLocations = null; } }
②、解析路劲
/** * Resolve the given path, replacing placeholders with corresponding * environment property values if necessary. Applied to config locations. * @param path the original file path * @return the resolved file path * @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment#resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String) */ protected String resolvePath(String path) { return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path); }
3、AbstractPropertyResolver
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { if (this.strictHelper == null) { this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false); } return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper); }
上述方法主要做了两件事 :
①、初始化占位符解析器
createPlaceholderHelper : 主要是初始化占位符的常量,eg : 前缀 ${ 后缀} and so on
②、调用私有方法---替换占位符具体值
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) { return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() { @Override public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) { return getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName); } }); }
4、占位符 key - > value ,
实现PropertyPlaceholderHelper内部接口PlaceholderResolver方法resolvePlaceholder。找到占位符key对应的value,为下文替换key埋下伏笔
protected String getPropertyAsRawString(String key) { return getProperty(key, String.class, false); }
代码太多了,这里只给出重点

protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) { boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled(); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(String.format("getProperty(\"%s\", %s)", key, targetValueType.getSimpleName())); } if (this.propertySources != null) { for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug(String.format("Searching for key ‘%s‘ in [%s]", key, propertySource.getName())); } Object value; if ((value = propertySource.getProperty(key)) != null) { Class<?> valueType = value.getClass(); if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) { value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value); } if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug(String.format("Found key ‘%s‘ in [%s] with type [%s] and value ‘%s‘", key, propertySource.getName(), valueType.getSimpleName(), value)); } if (!this.conversionService.canConvert(valueType, targetValueType)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "Cannot convert value [%s] from source type [%s] to target type [%s]", value, valueType.getSimpleName(), targetValueType.getSimpleName())); } return this.conversionService.convert(value, targetValueType); } } } if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug(String.format("Could not find key ‘%s‘ in any property source. Returning [null]", key)); } return null; }
5、占位符解析器, 解析并替换具体值得逻辑在这里
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) { Assert.notNull(value, "‘value‘ must not be null"); return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<String>()); }
递归查找占位符
protected String parseStringValue( String strVal, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(strVal); int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix); while (startIndex != -1) { int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex); if (endIndex != -1) { String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex); String originalPlaceholder = placeholder; if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Circular placeholder reference ‘" + originalPlaceholder + "‘ in property definitions"); } // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key. placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); // 递归查找 // Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key... String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder); if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) { int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator); if (separatorIndex != -1) { String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex); String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length()); propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder); // 这里是调用第四步骤的实现PropertyPlaceholderHelper内部接口PlaceholderResolver方法resolvePlaceholder :占位符 key -> value if (propVal == null) { propVal = defaultValue; } } } if (propVal != null) { // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the // previously resolved placeholder value. propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal); // 替换占位符具体值 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Resolved placeholder ‘" + placeholder + "‘"); } startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length()); } else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { // Proceed with unprocessed value. startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length()); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder ‘" + placeholder + "‘" + " in string value \"" + strVal + "\""); } visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder); } else { startIndex = -1; } } return result.toString(); }
findPlaceholderEndIndex 查找占位符在所在字符串后缀的位置

private int findPlaceholderEndIndex(CharSequence buf, int startIndex) { int index = startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(); int withinNestedPlaceholder = 0; while (index < buf.length()) { if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, this.placeholderSuffix)) { if (withinNestedPlaceholder > 0) { withinNestedPlaceholder--; index = index + this.placeholderSuffix.length(); } else { return index; } } else if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, this.simplePrefix)) { withinNestedPlaceholder++; index = index + this.simplePrefix.length(); } else { index++; } } return -1; }
StringUtis.substringMatch 匹配当前位置的字符是否为占位符后缀

public static boolean substringMatch(CharSequence str, int index, CharSequence substring) { for (int j = 0; j < substring.length(); j++) { int i = index + j; if (i >= str.length() || str.charAt(i) != substring.charAt(j)) { return false; } } return true; }