目标检测方法——SSD
SSD论文阅读(Wei Liu——【ECCV2016】SSD Single Shot MultiBox Detector)
目录
- 作者
- 文章的选择原因
- 方法概括
- 方法细节
- 相关背景补充
- 实验结果
- 与相关文章的对比
- 总结
作者

文章的选择原因
- 性能好,single stage
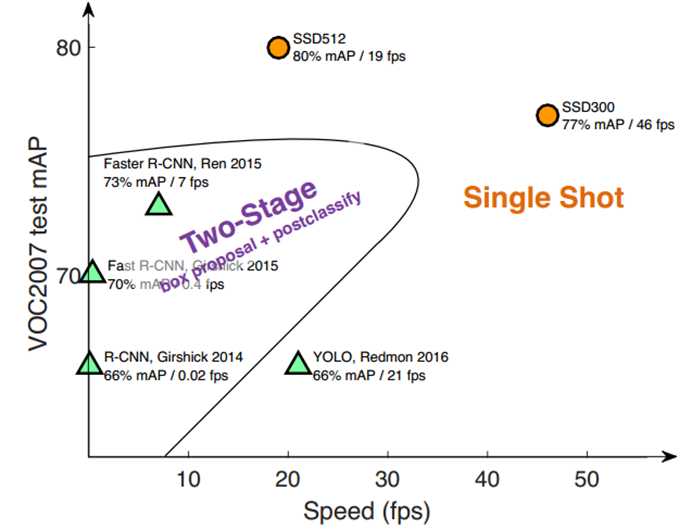
方法概括
-
文章的方法介绍
- SSD主要用来解决目标检测的问题(定位+分类),即输入一张待测图像,输出多个box的位置信息和类别信息
- 测试时,输入一张图像到SSD中,网络输出一个下图最右边的tensor(多维矩阵),对该矩阵进行非极大值抑制(NMS)就能得到每个目标的位置和label信息
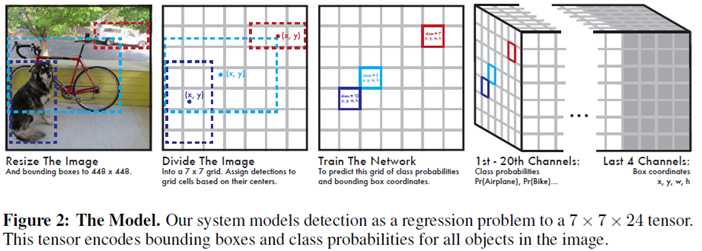
Figure2的最右图的1th-20th Channel表示类别,每一个Channel上的map对应原图,last 4 channel的每一个map分别对应x,y,w,h的偏移量。最后4个通道可以确定一个box的位置信息,前20个通道确定类别信息。
-
方法的pipeline和关键点
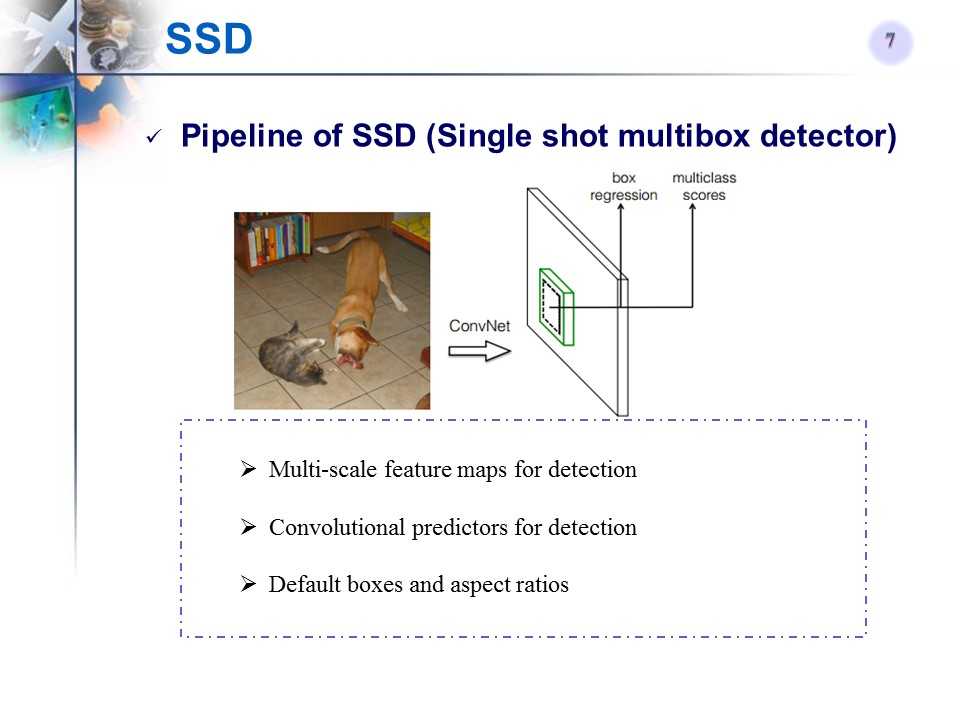
方法细节
-
模型结构
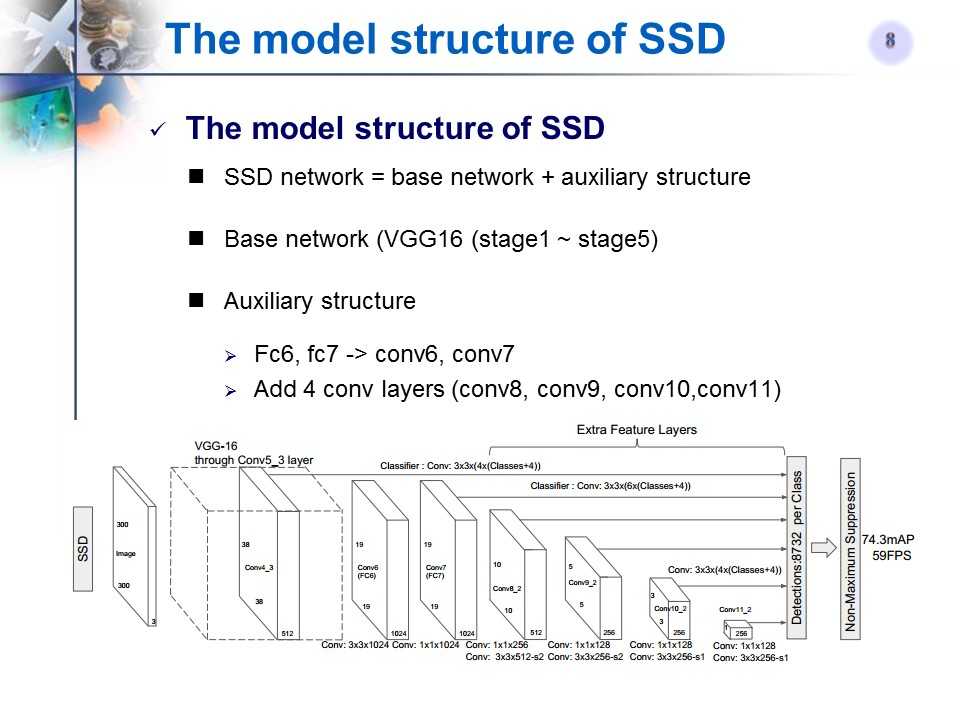
-
多尺度特征图
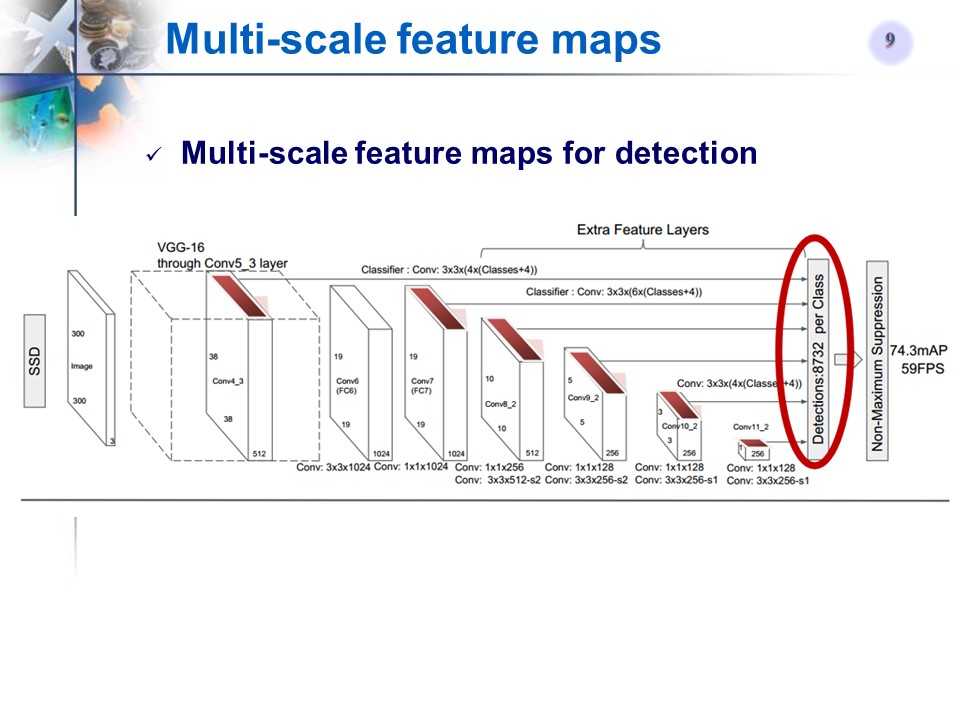
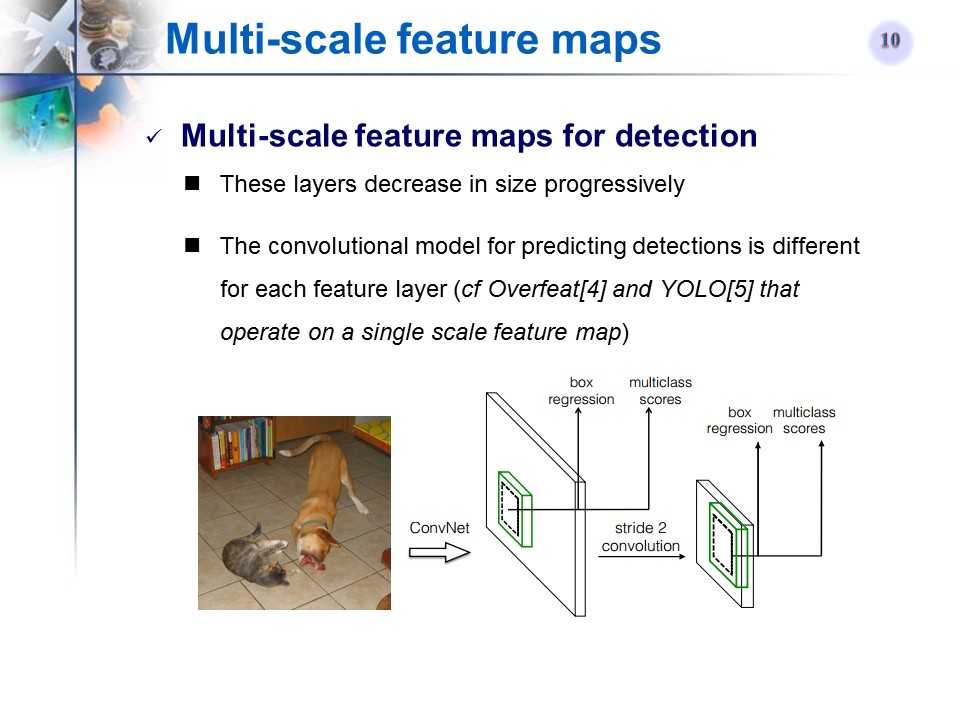
-
用来预测的卷积滤波器
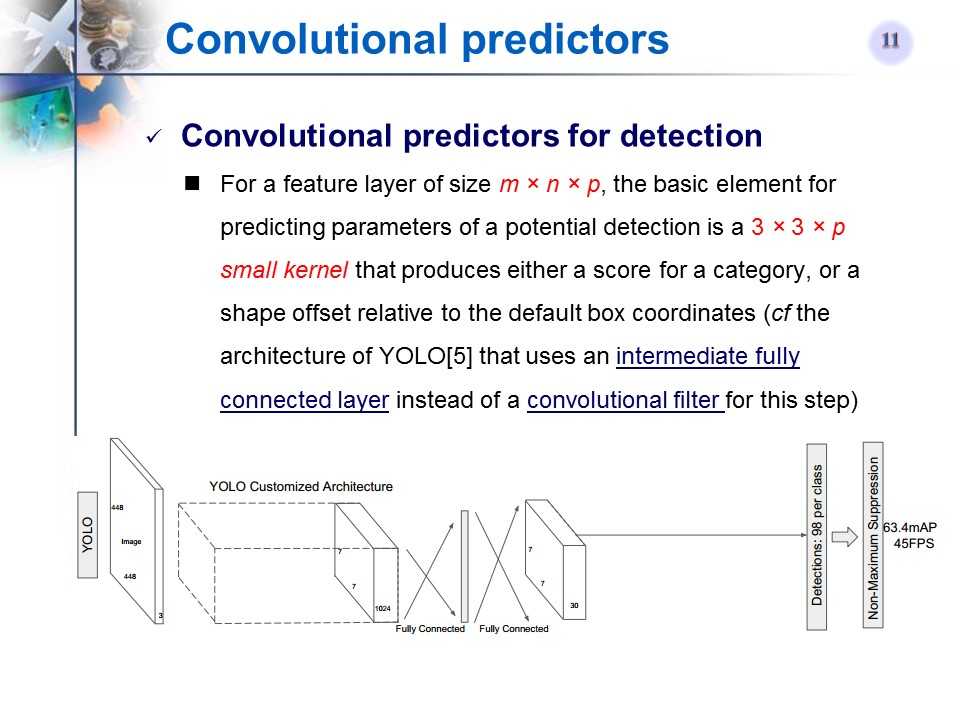
-
defaul box

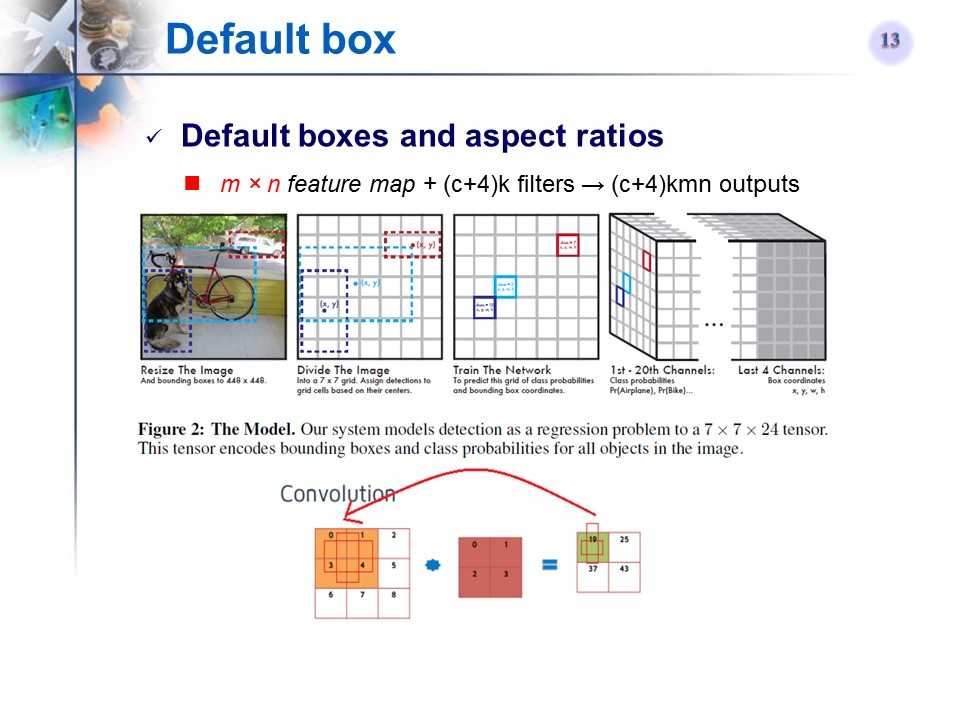
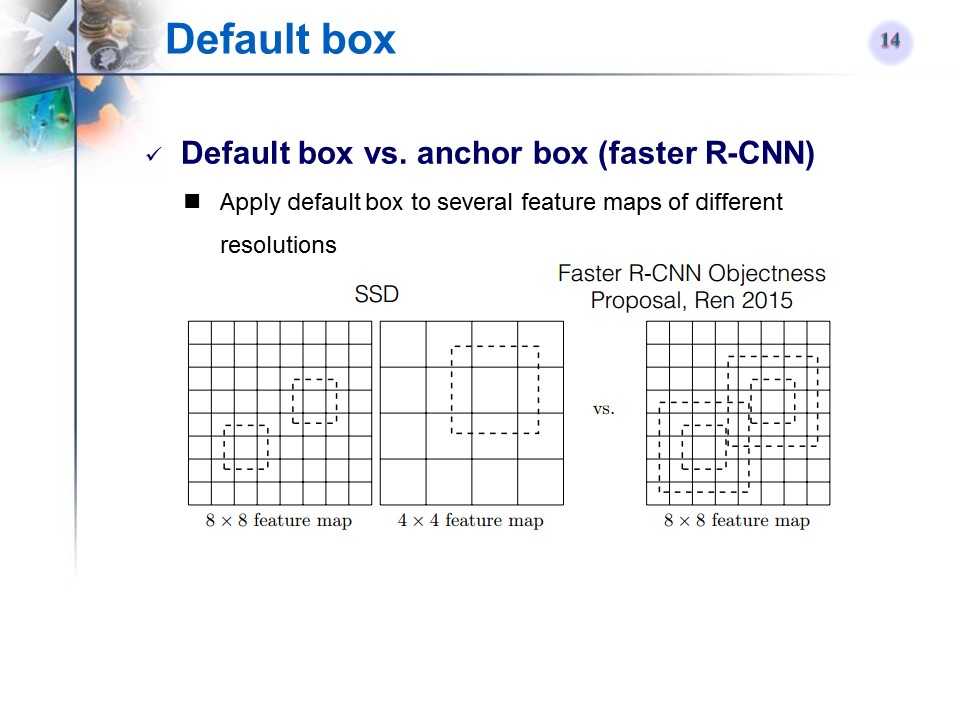
-
groundTruth的标定,损失函数

-
default box和尺度的选择

-
SSD的训练——Hard negative mining

-
SSD的训练——数据扩增
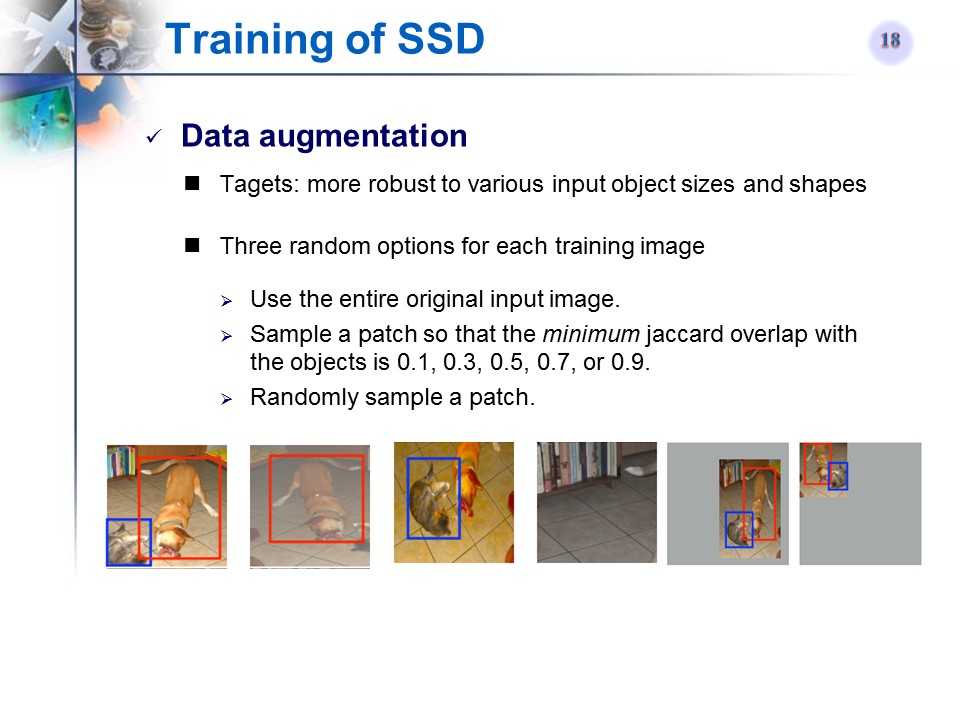
相关背景补充
-
Atrous算法(hole算法)
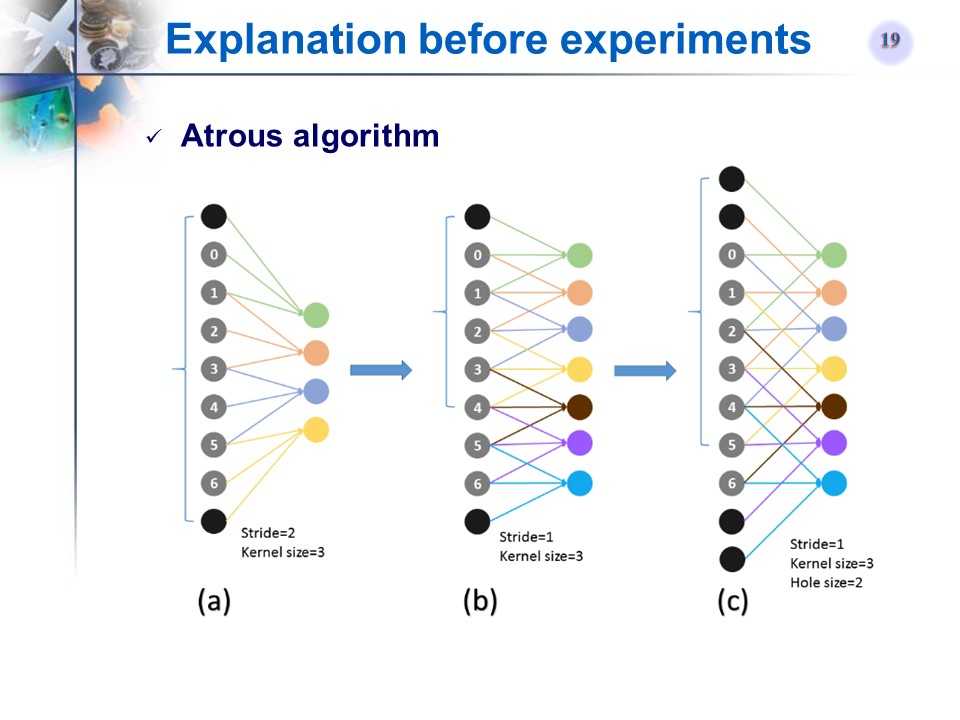
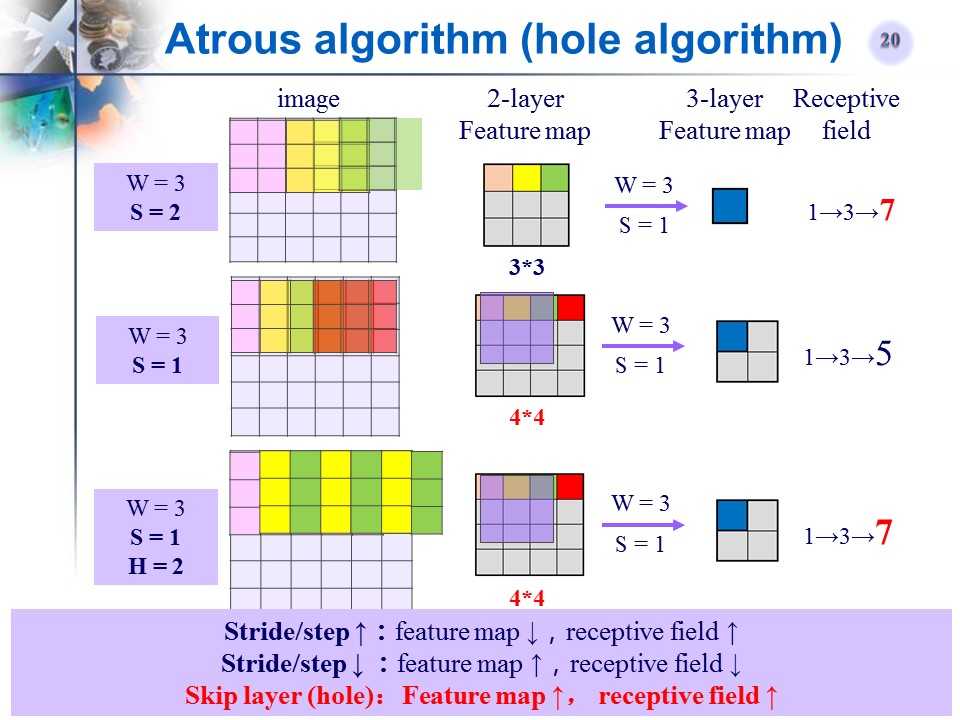
-
FPS/SPF, Jaccard overlap
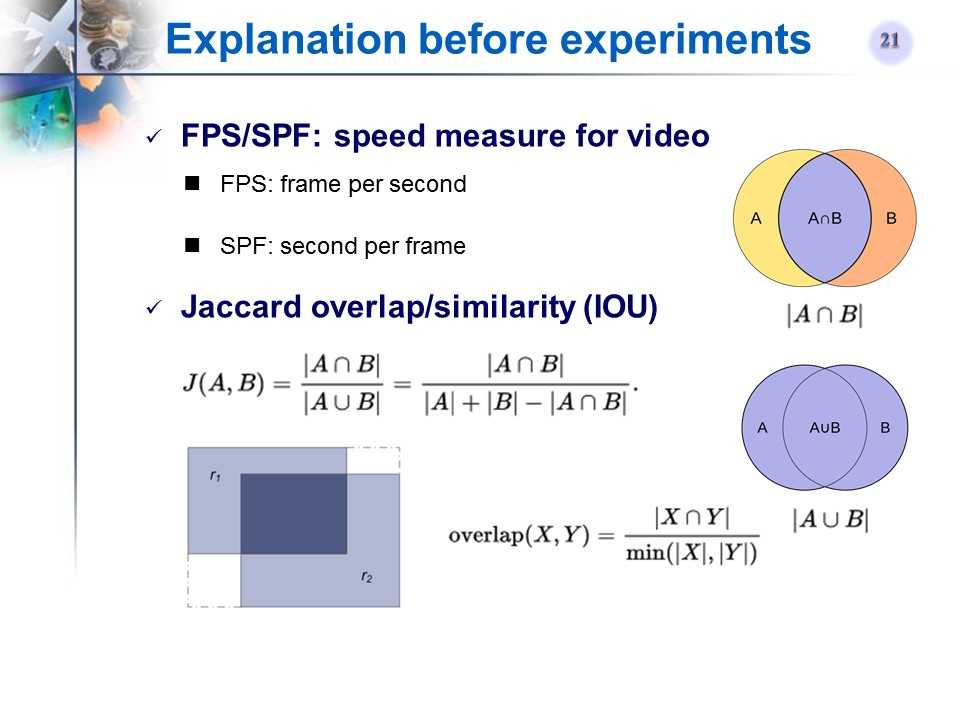
-
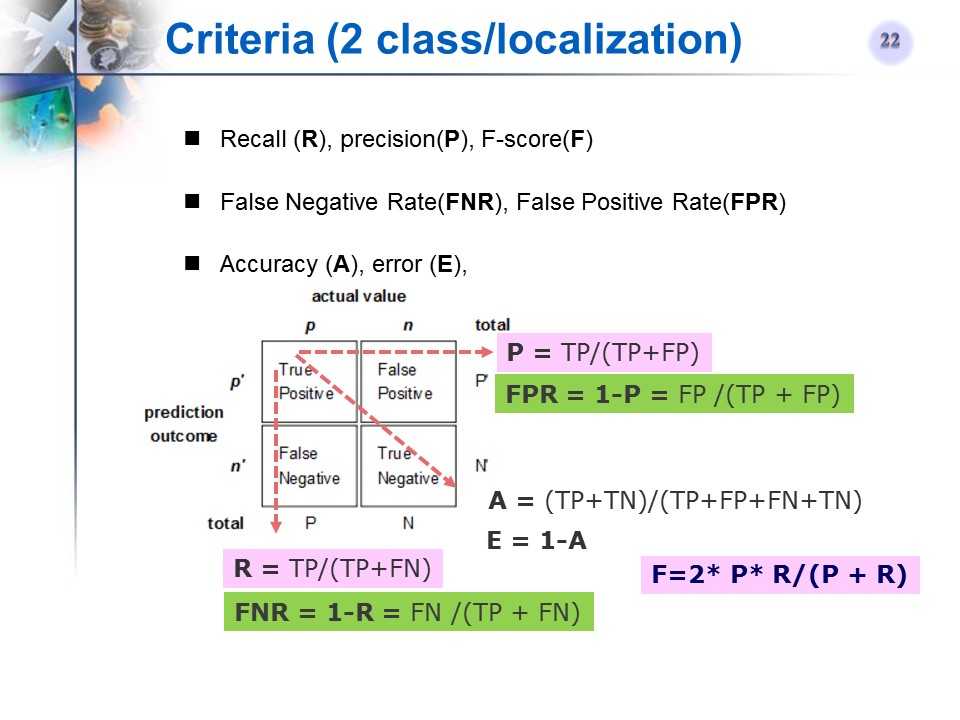
二类分类/检测常用的评价标准 (recall, precision, f-measure, accuracy, error, PR曲线和ROC曲线,AP,AUC)
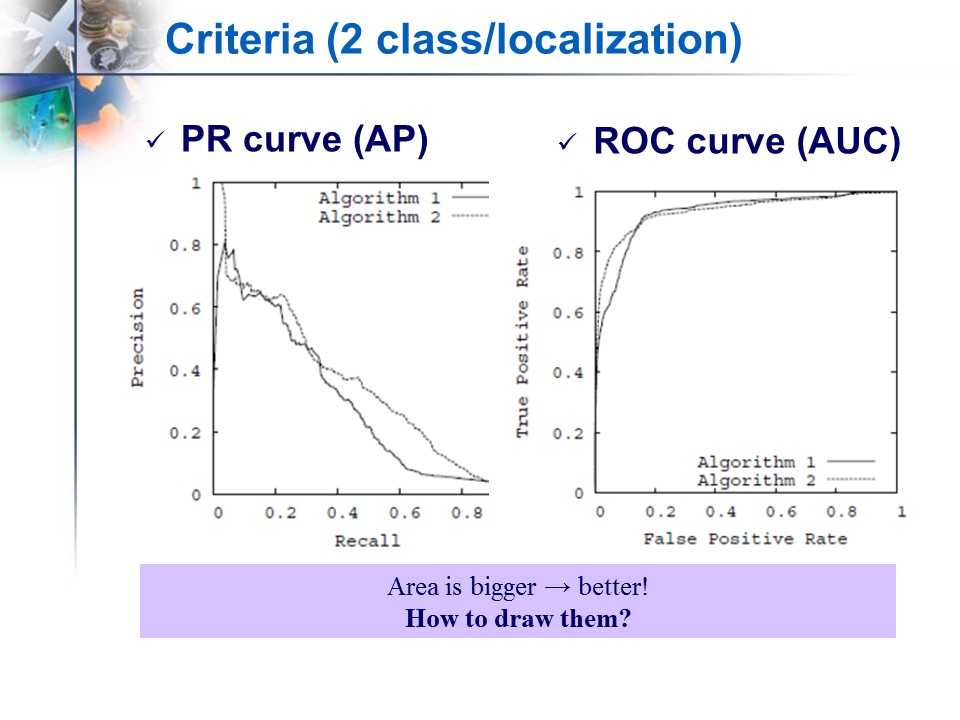
-
ImageNet多类分类的评价标准
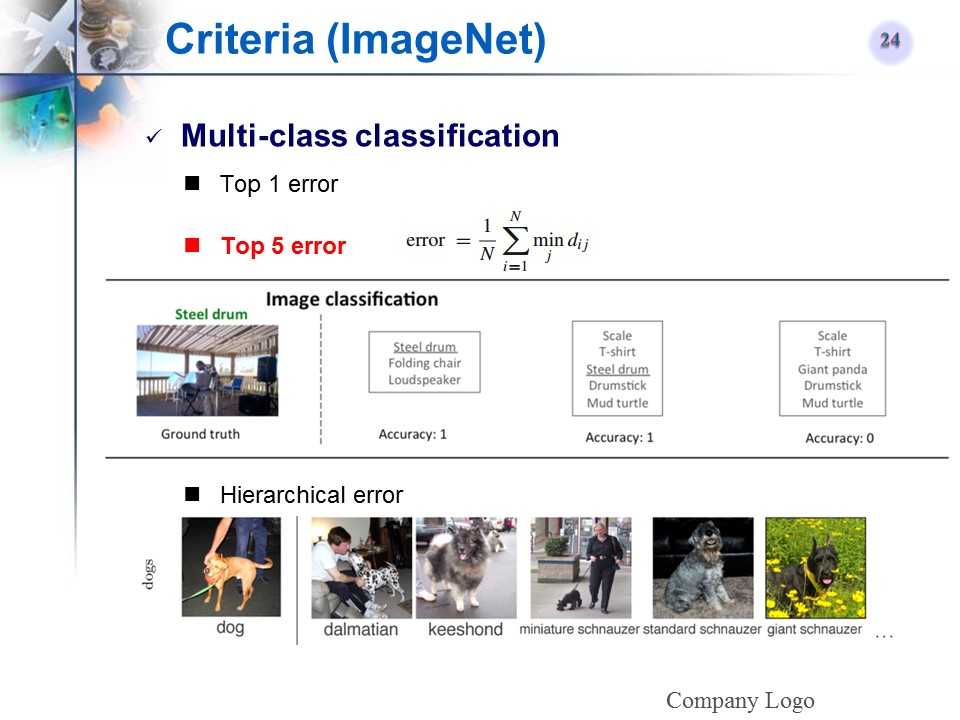
-
ImageNet单目标检测的评价标准
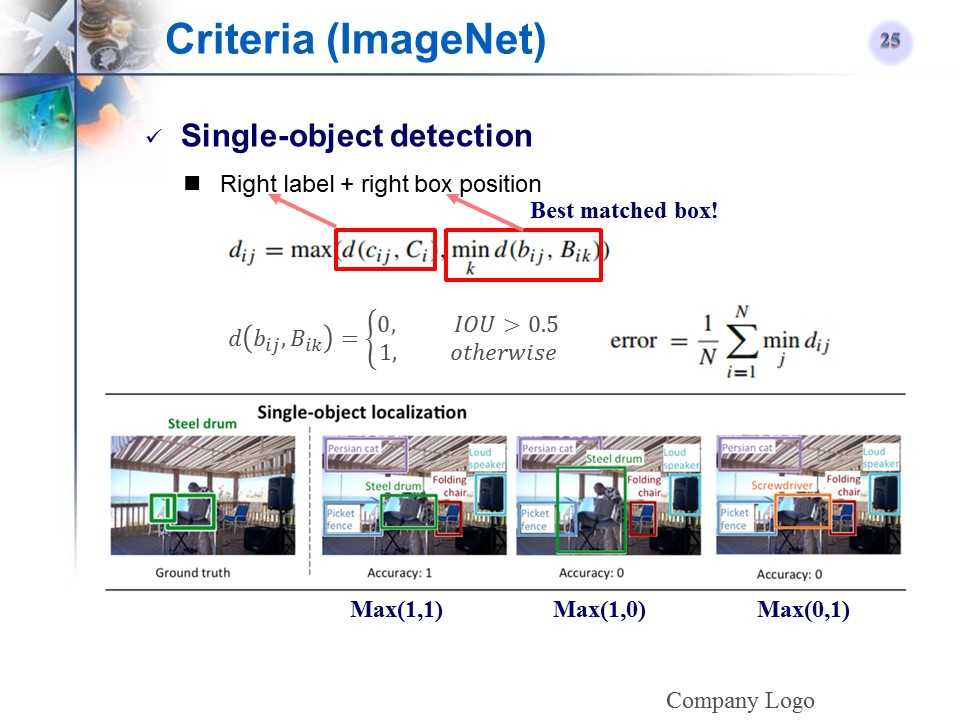
-
ImageNet(多)目标检测的评价标准
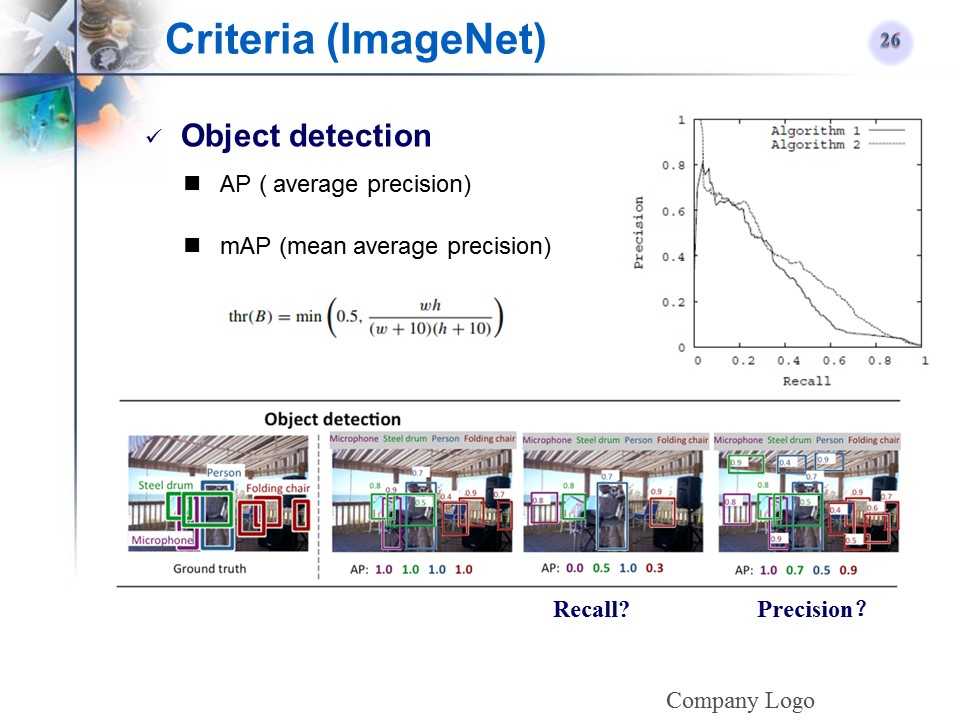
实验结果
-
PASCAL VOC2007 test detection结果
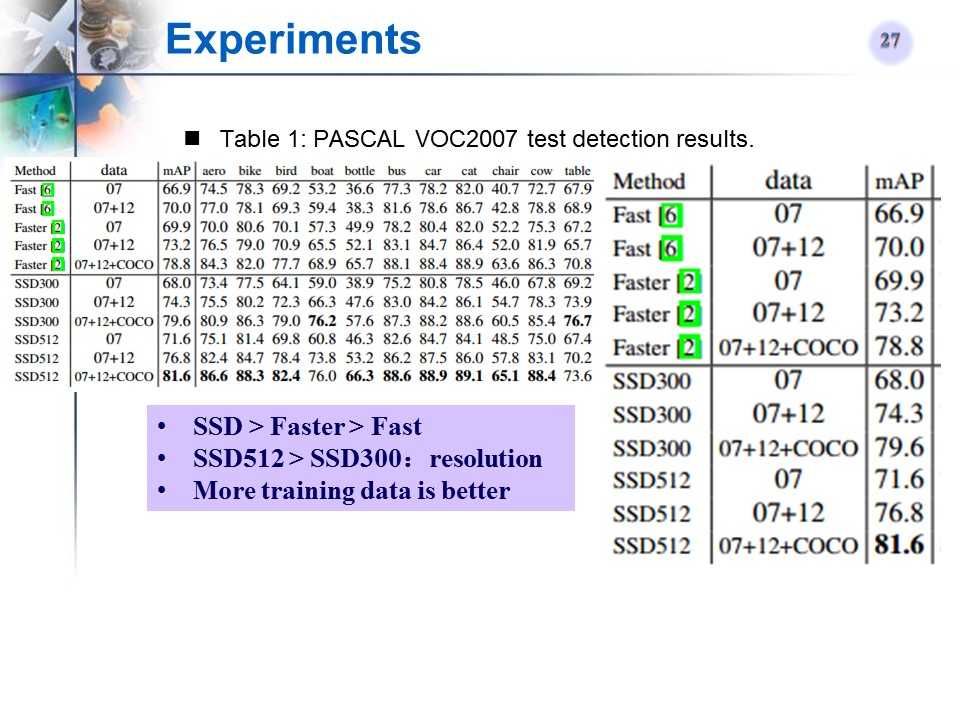
-
使用数据扩增、多尺度default box、atrous算法的对比效果
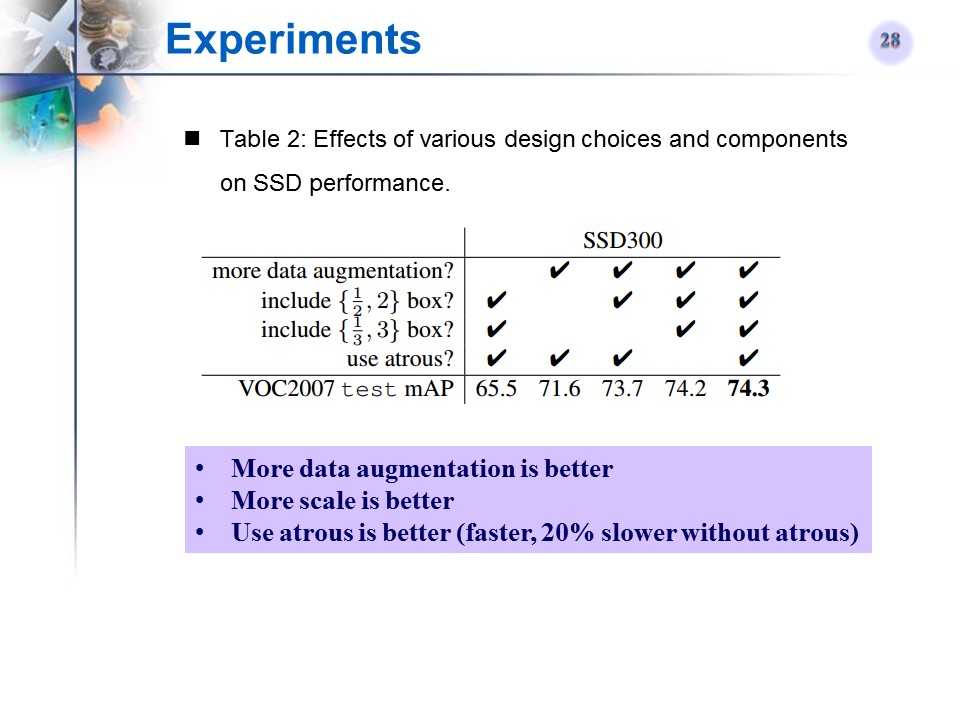
-
SSD512在某类Ianimals)上的检测性能可视化
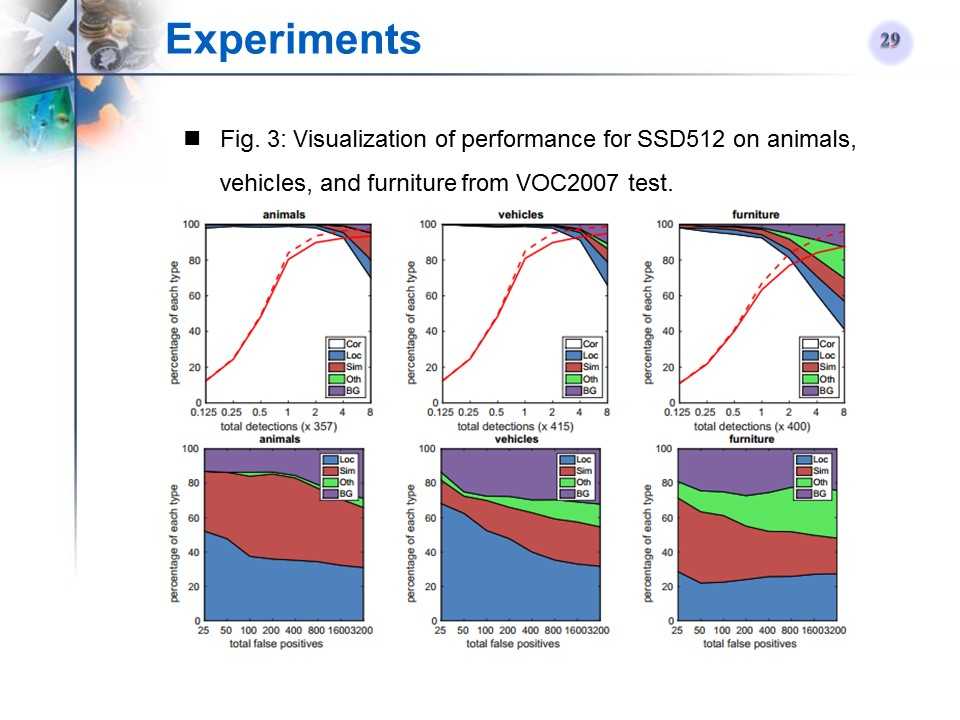
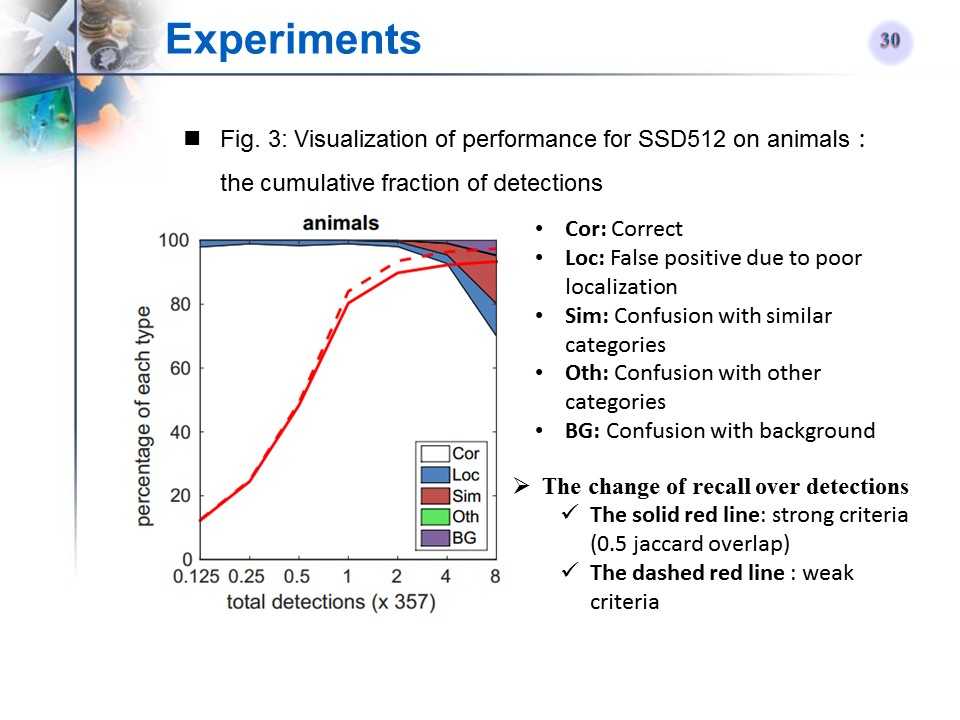
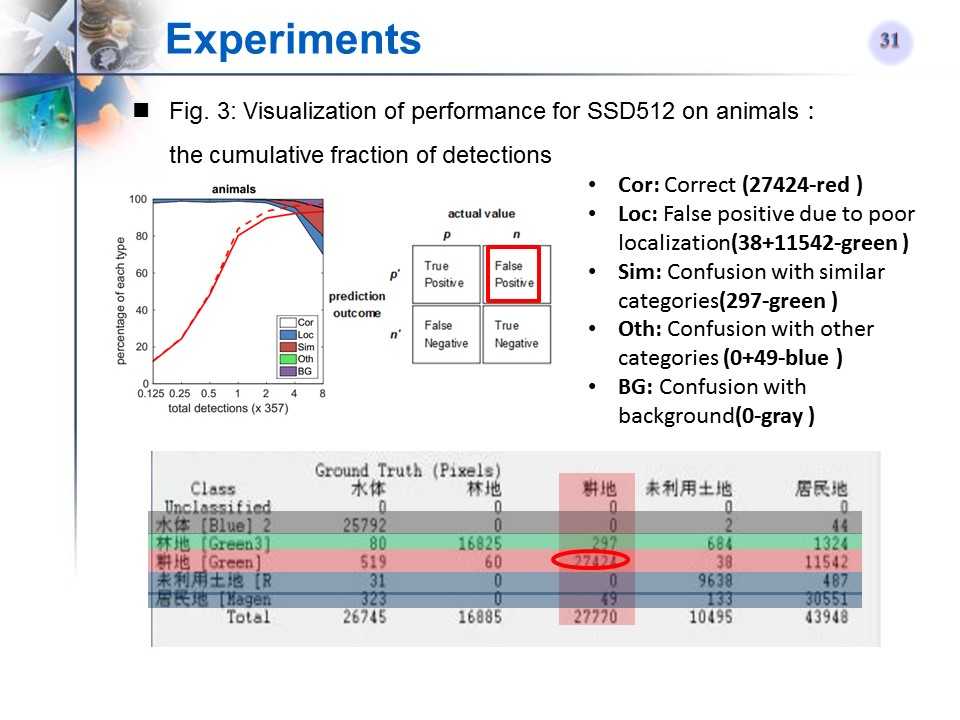
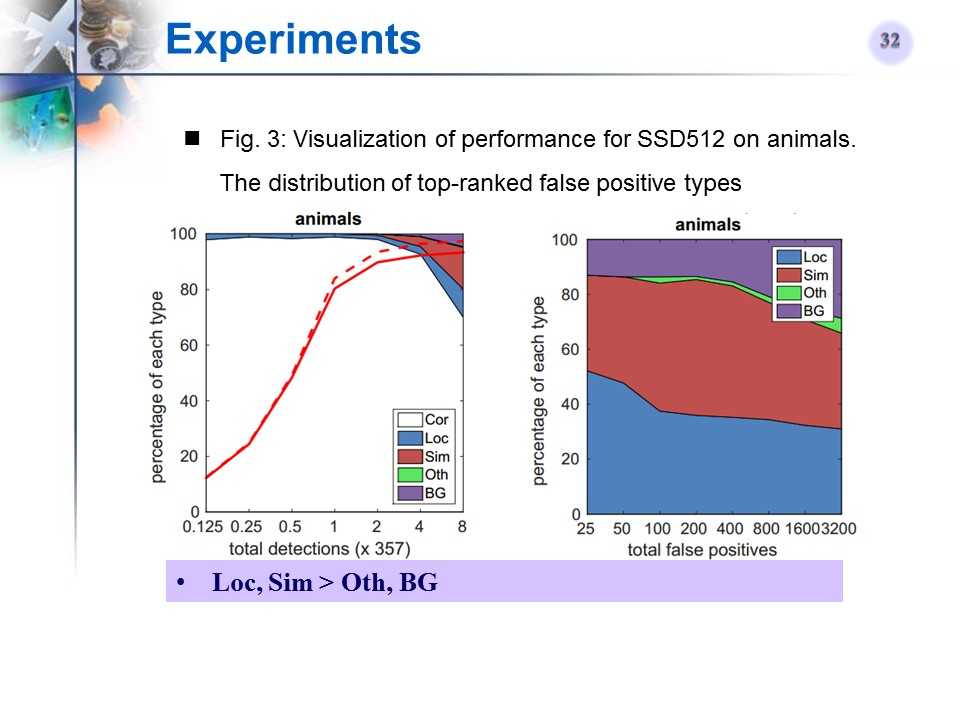
-
SSD对于目标大小的敏感性实验
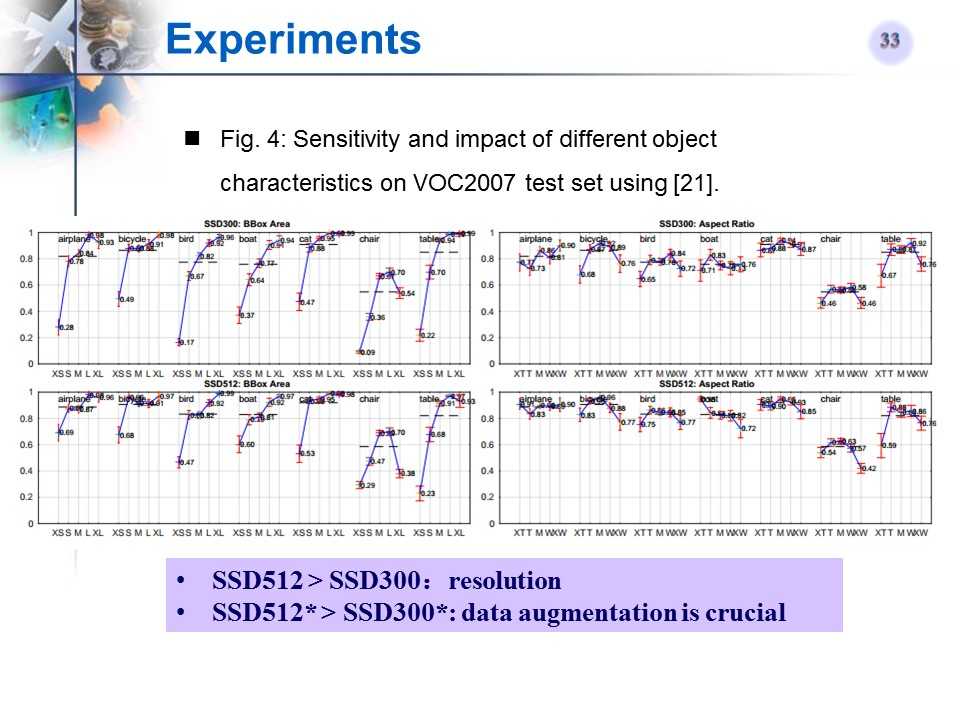
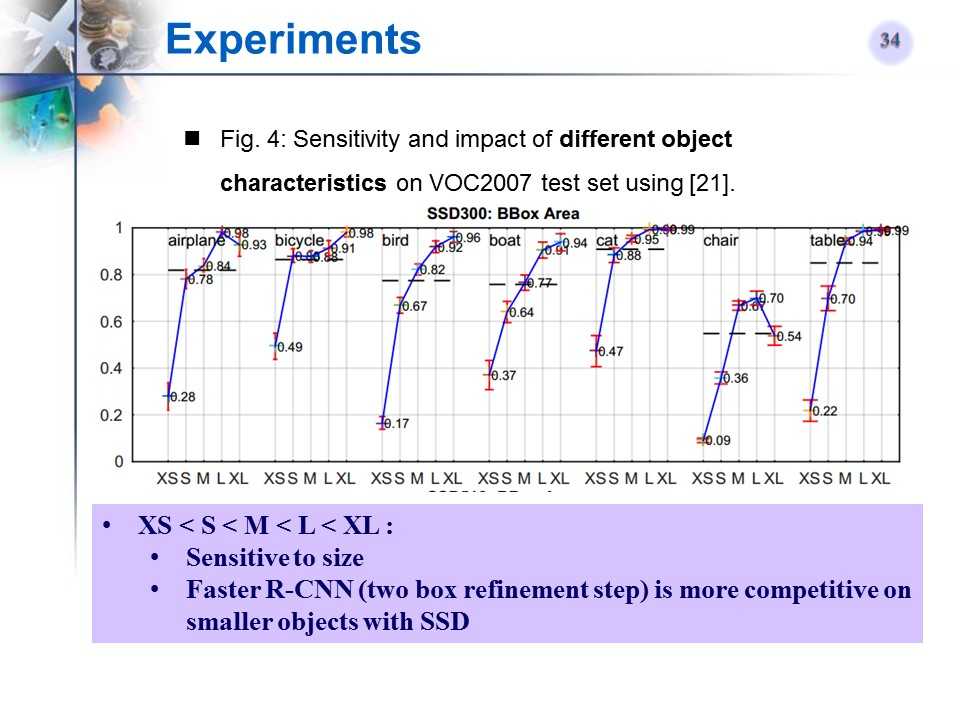
-
SSD使用的feature map的个数对结果的影响
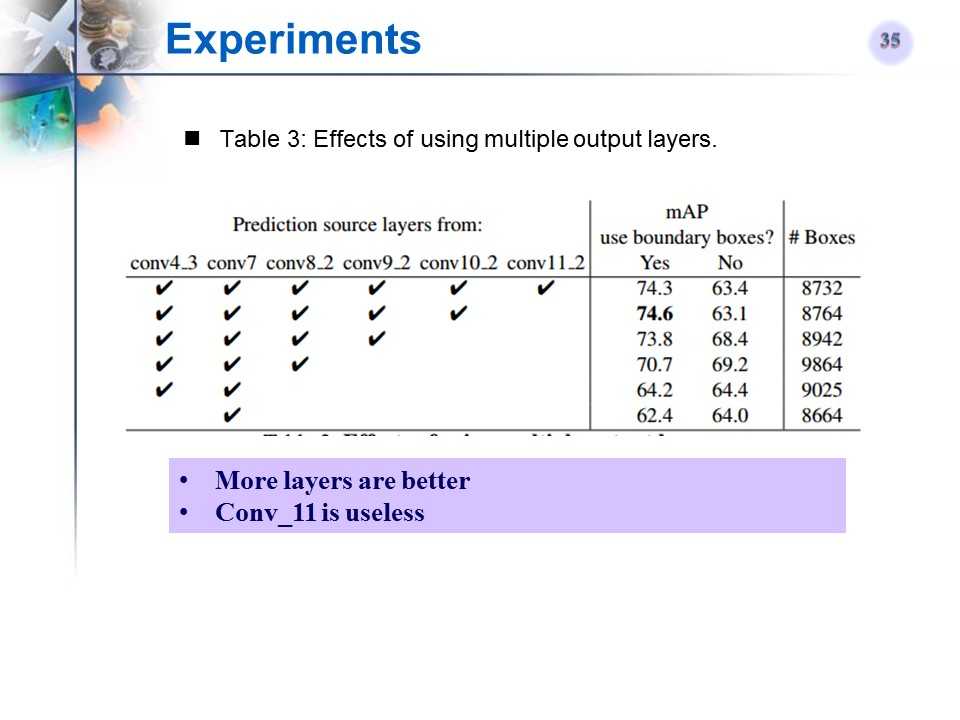
-
示例结果

-
时间和速度

与相关文章的对比
-
原始R-CNN方法的变形
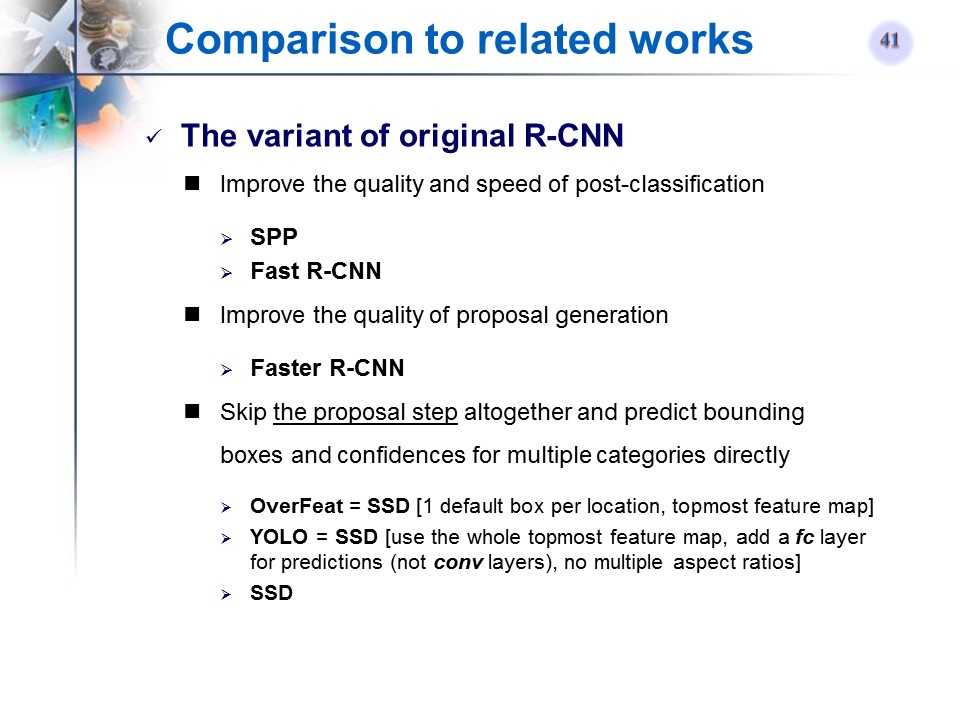
-
Faster R-CNN和SSD对比
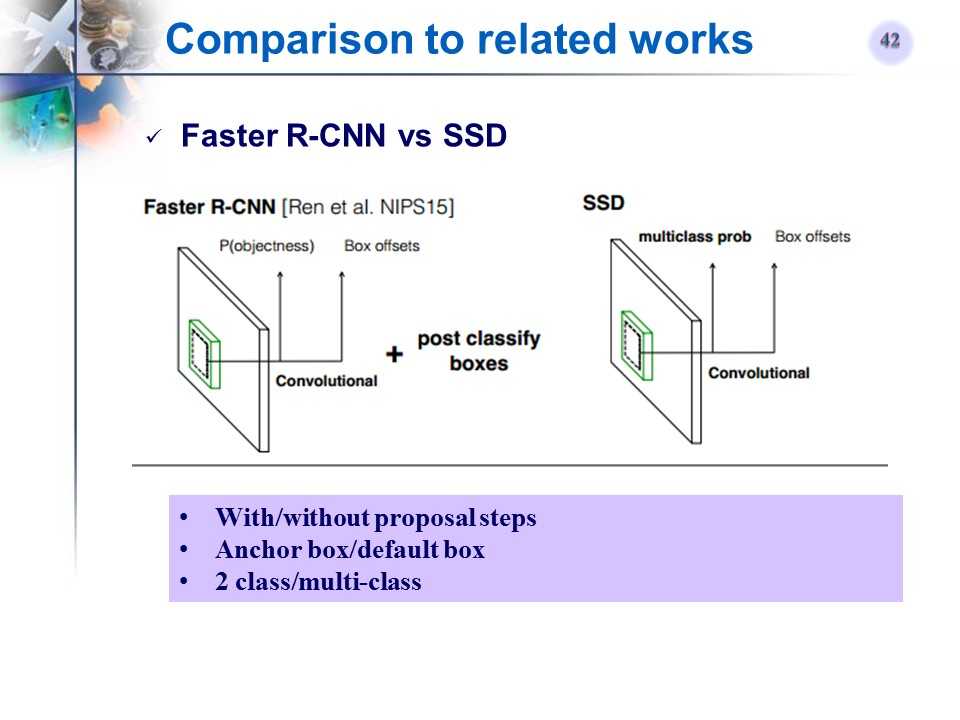
-
YOLO和SSD对比
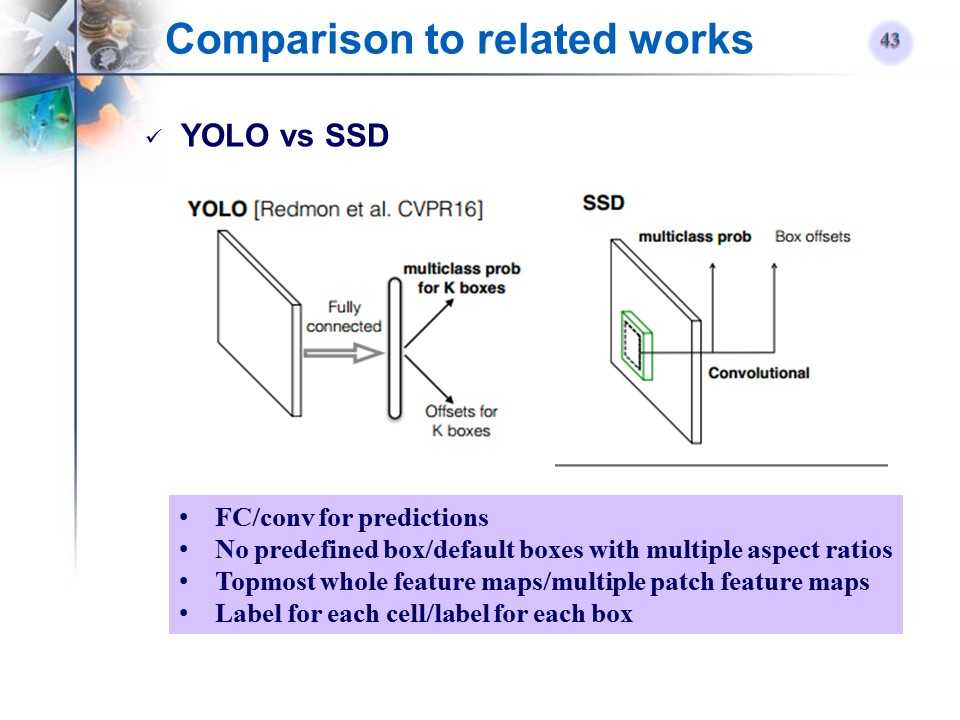
总结
-
文章贡献
- SSD, a single-shot detector for multiple categories (faster than YOLO, accurate as Faster R-CNN)
- The core of SSD is predicting category scores and box offsets for a fixed set of default bounding boxes using small convolutional filters applied to multiple feature maps from different layers
- Experimental evidence: high accuracy, high speed, simple end-to-end training (single shot)
-
SSD对于其他方法的改进的关键点
-
- Using a small convolutional filter to predict object categories and offsets in bounding box locations
- Using separate predictors (filters) for different aspect ratio detections
- Using multiple layers for prediction at different scales (apply these filters to multiple feature maps to perform detection at multiple stages)
文章来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/lillylin/p/6207292.html