5.2.5 Fragment实例精讲——新闻(购物)类App列表Fragment的简单实现
本节引言:
相信大家对点击列表,然后进入详情这种App并不陌生吧,在购物类App和新闻类App中最为常见: 下面我们简单来讲一下流程逻辑!
1.逻辑流程讲解:
刚好公司测试妹子的测试机上装了楚楚街9块9的APP,呵呵,直接就照这个来研究吧:

嘿嘿,市面上很多APP都是这种样子的,而这个可以用我们学到的Fragment来实现: 可能gif动画看不清,笔者用界面原型工具画个大概吧:
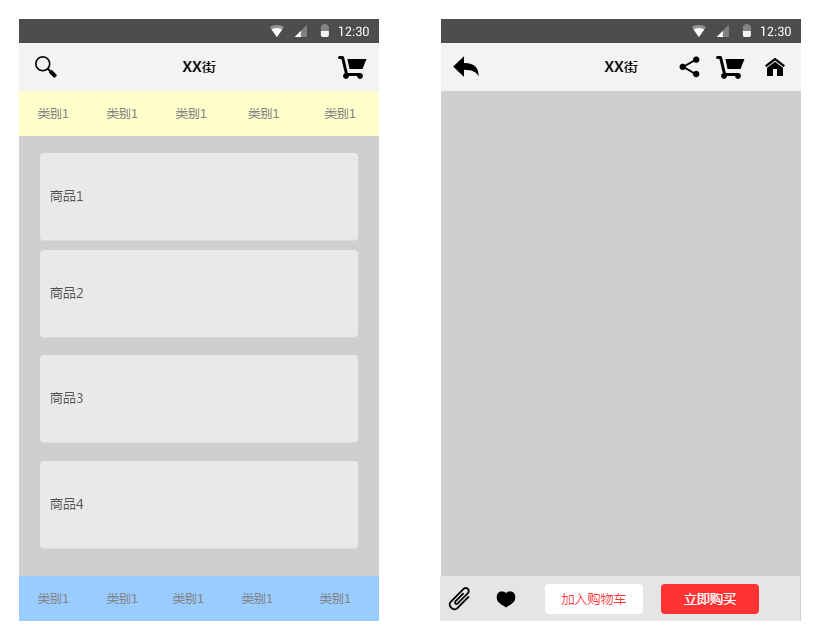
大概就这样,中间区域是一个布局容器,一般是FrameLayout,然后我们将一个Fragment replace 到这个容器中或者add也行,而这个Fragment中有一个listview,当我们点击这个ListView中的一项, 中间容器中的Fragment就会被replace成对应详细信息的Fragment所替代,如果我们只是replace的话, 就不会保存第一个Fragment的状态,用户又得从头开始浏览,这肯定是很不方便的,这里我们可以 通过Fragment栈的addtobackStack和popbackstack来解决这个问题!当replace的同时,我们将被替换 的Fragment添加到stack中,当用户点击回退按钮时,调用popbackstack弹出栈,具体实现见下述代码 示例!
2.代码示例:简单新闻类APP列表和内容切换的实现
运行效果图:

实现代码:
Step 1:先把两个Fragment以及Activity的布局实现了
fg_newlist.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list_news"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
fg_context.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColor="@color/blue"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
activity_main.xml:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="56dp"
android:background="@color/blue"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:text="新闻列表"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:gravity="center"/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fl_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@id/txt_title"/>
</RelativeLayout>
Step 2:实现我们的业务Bean类和自定义BaseAdapter类:
Data.java:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/6 0006.
*/
public class Data {
private String new_title;
private String new_content;
public Data(){}
public Data(String new_title, String new_content) {
this.new_title = new_title;
this.new_content = new_content;
}
public String getNew_title() {
return new_title;
}
public String getNew_content() {
return new_content;
}
public void setNew_title(String new_title) {
this.new_title = new_title;
}
public void setNew_content(String new_content) {
this.new_content = new_content;
}
}
MyAdapter.java:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/6 0006.
*/
public class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private List<Data> mData;
private Context mContext;
public MyAdapter(List<Data> mData, Context mContext) {
this.mData = mData;
this.mContext = mContext;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mData.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder viewHolder;
if(convertView == null){
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.list_item,parent,false);
viewHolder = new ViewHolder();
viewHolder.txt_item_title = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.txt_item_title);
convertView.setTag(viewHolder);
}else{
viewHolder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
viewHolder.txt_item_title.setText(mData.get(position).getNew_title());
return convertView;
}
private class ViewHolder{
TextView txt_item_title;
}
}
Step 3:MainActivity的实现
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView txt_title;
private FrameLayout fl_content;
private Context mContext;
private ArrayList<Data> datas = null;
private FragmentManager fManager = null;
private long exitTime = 0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = MainActivity.this;
fManager = getFragmentManager();
bindViews();
datas = new ArrayList<Data>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
Data data = new Data("新闻标题" + i, i + "~新闻内容~~~~~~~~");
datas.add(data);
}
NewListFragment nlFragment = new NewListFragment(fManager, datas);
FragmentTransaction ft = fManager.beginTransaction();
ft.replace(R.id.fl_content, nlFragment);
ft.commit();
}
private void bindViews() {
txt_title = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txt_title);
fl_content = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.fl_content);
}
//点击回退键的处理:判断Fragment栈中是否有Fragment
//没,双击退出程序,否则像是Toast提示
//有,popbackstack弹出栈
@Override
public void onBackPressed() {
if (fManager.getBackStackEntryCount() == 0) {
if ((System.currentTimeMillis() - exitTime) > 2000) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "再按一次退出程序",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
exitTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
} else {
super.onBackPressed();
}
} else {
fManager.popBackStack();
txt_title.setText("新闻列表");
}
}
}
Step 4:列表Fragment的实现:
NewListFragment.java:
package com.jay.fragmentdemo4;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/6 0006.
*/
public class NewListFragment extends Fragment implements AdapterView.OnItemClickListener {
private FragmentManager fManager;
private ArrayList<Data> datas;
private ListView list_news;
public NewListFragment(FragmentManager fManager, ArrayList<Data> datas) {
this.fManager = fManager;
this.datas = datas;
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fg_newlist, container, false);
list_news = (ListView) view.findViewById(R.id.list_news);
MyAdapter myAdapter = new MyAdapter(datas, getActivity());
list_news.setAdapter(myAdapter);
list_news.setOnItemClickListener(this);
return view;
}
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
FragmentTransaction fTransaction = fManager.beginTransaction();
NewContentFragment ncFragment = new NewContentFragment();
Bundle bd = new Bundle();
bd.putString("content", datas.get(position).getNew_content());
ncFragment.setArguments(bd);
//获取Activity的控件
TextView txt_title = (TextView) getActivity().findViewById(R.id.txt_title);
txt_title.setText(datas.get(position).getNew_content());
//加上Fragment替换动画
fTransaction.setCustomAnimations(R.anim.fragment_slide_left_enter, R.anim.fragment_slide_left_exit);
fTransaction.replace(R.id.fl_content, ncFragment);
//调用addToBackStack将Fragment添加到栈中
fTransaction.addToBackStack(null);
fTransaction.commit();
}
}
Step 5:内容Fragment的实现:
NewContentFragment.java:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/6 0006.
*/
public class NewContentFragment extends Fragment {
NewContentFragment() {
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fg_content, container, false);
TextView txt_content = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.txt_content);
//getArgument获取传递过来的Bundle对象
txt_content.setText(getArguments().getString("content"));
return view;
}
}
代码很简单,就不慢慢解释了~
本节小结:
因为时间的关系,并没有详细的去做过多的讲解,示例代码也很简单,方便各位初学者理解! 如果要用到实际项目中还需要对此进行一番修改~!好的,本节就到这里,谢谢~